- Yawning is a phylogenetically old,
stereotyped event that occurs alone or
assiociated with stretching and/or penile
erection in humans and in animals from reptiles
to birds and mammals under different conditions.
Although its physiological function is still
unknown, yawning is under the control of
several
neurotransmitters and neuropetides at the
central level as this short overview of
litterature on neurochemistry of yawning
show
-
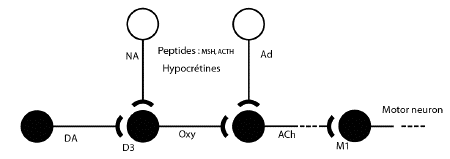
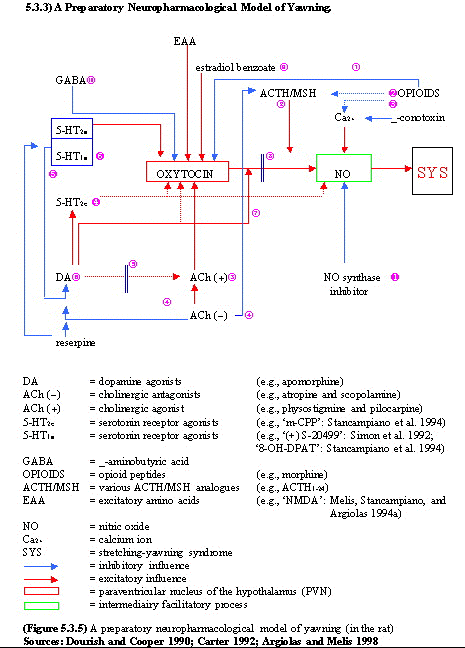
- Among these substances, the best known are
dopamine,
excitatory
aminoacids, acetylcholine, serotonin,
nitric oxyde, adrenocorticotropic
hormone-related petides and oxytocin, that
falicitate yawning and opiod peptides that
inhibit this behavioral reponse.
-
- Some of the above compounds interact in the
paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to
control yawning. This hypothalamic nucleus
contains the cell bodies of oxytocinergic
neurons projecting to extra-hyopthalamic brain
areas that play a key role in the expression of
this behavioral event.
-
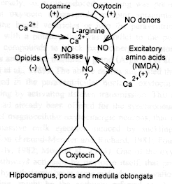
- When activate by dopamine, ecxitatory
aminoacids and oxytocin itself, the neurons
facilitate yawning by releasing oxytocin at
sites distant form the paraventricular nucleus,
i.e. the hippocampus, the pons and/or the
medulla oblongata. Conversely, actviation of
these neurons by dopamine, oxycocin or
excitatory aminoacids, is antagonized by opioid
peptides, that, in turn, prevent the yawning
reponse.
-
- The activation and inhibition, respectively
of these oxytocinergic neurons is related to
concomitant increase and decrease, respectively,
of paraventricular nitric oxide synthase
activity. However, other neuronal systems in
addiction to the central paraventricular
oxytocinergic neurons are involved in the
control of yawning, since they do seem to be
involved in the expression of ywaning induced by
the stimulation of acetylcholine or
sreotononergic receptors, nor by
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and related
peptides. Nitric oxide is also involved in the
induction of yawing by the latter compounds and
neuronal links, for instance between dopamine
and acetylcholine and dopamine and serotonin,
seem to be involved in the yawnin repose.
-
- Finally, other neurotransmitters, i.e.
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and noradrenaline
and neuropeptides, i.e. neurotensin and
luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH),
influence this behavioral reponse.
-
- In conclusion, in spite of somme recent
progress, little is known of, and more as to be
to identify the neurochemical mechanism
underlying yawning at the central level.
-
-
-
- Collins
G, JM Witkin et al Dopamine agonist-induced
yawning in rats: a dopamine d3 receptor mediated
behavior J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005
-
- Argiolas
A, Melis Mr, Bernard B
departement of neuroscience, University of
Cagliari, Italy
- The neuropharmacology of yawning
Eur Pharmacol 1998; 343; 1;
1-16
- télécharger
l'intégralité de cet article au
format pdf
-
- -Sanna
F, Succu S, Melis MR, Argiolas A. Dopamine
agonist-induced penile erection and yawning:
Differential role of D(2)-like receptor subtypes
and correlation with nitric oxide production in
the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
of male rats. Behav Brain Res. 2012
-
- ........................
 ......
...... ......
......
-
- Askenasy
JJ Is yawning an arousal defense reflex
?
- Schematic
model of neurotransmitter circuits that are
involved in the three states of
vigilance
- Yawning
and penile erection: central
dopamine-oxytocin-adrenocorticotropin
connection Argiolas A
- Yawning:
neurochemistry, physiology and pathology
1987 Argiolas A, Melis MR, Gessa GL
-
-
- Flavio Aloe
Yawning
- Daquin G, J
Micallef, O Blin
Yawning
- Smith EO
Yawning: an
evolutionary perspective
- Why do
people yawn ?
- Neural
basis of drug induced yawning Cooper SJ,
Dourish CT in Neurobiology of Stereotyped
Behaviour
-
|


 ......
......
......
......