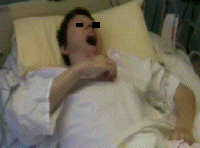
 = video
= video
-
- Tremor
in
Prodromal Parkinson's
Disease
-
- - Aaron
S, Al Hashmi A. Parakinesia Brachialis
Oscitans due to Brain Stem Infarct. Dubai
Medical journal - Case report &endash; May
2019
-
- - Alstadhaug
KB. Et Gjesp fra fortiden
(Norvégien et traductions)
-
- -Alves
NP, de Carvalho M, Reimão S, Castro J,
Fonseca AC, Canhão P. Voluntary
control of a plegic limb during yawning. J of
Neurol 2018;265(2):433-435
-
- -Blin
O, Rascol O, Azulay JP, Serratrice G,
Nieoullon A. A single report of
hemiplegic arm stretching related to yawning:
further investigation using apomorphine
administration. J Neurol Sci.
1994;126:225-227.
-
- -Chowdhury
A, Datta AK, Biswas S, Biswas A.
Parakinesia Brachialis Oscitans &endash; a
Rare Post-Stroke Phenomenon. Tremor and Other
Hyperkinetic Movements. 2022; 12(1): 6.
-
- - De
Esacarra AR. De quelques
phénomènes curieux chez les
hémiplégiques. Thèse
Paris 1868
-
- -Jung
N, Ahn B et al. A case of parakinesia
brachialis oscitans. Clinical Neurology and
Neurosurgery. 2012;114(2):156-158.
-
- -de
Lima O, Munhoz R, Becker N, Teive H.
Parakinesia Brachialis Oscitans. Report of
three cases.Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
2012;18(2):204-206.
-
- -Isis
Claire Z.Y. Lim, Shermyn Neo. Parakinesia
Brachialis Oscitans: Old Sign, New Findings.
Stroke
2022;53:e60-e62.
-
- -Kang
P, Dhand A. Movement of a paralyzed arm
with yawning. Neurology.
2015;84(16):e118.
-
- -Lanari
A, Delbono O The yawning and stretching
sign in hemiplegics Medicina (B Aires)
1983;43(3):355-356
-
- -Na-Yeon
Jung ,Bo-Young Ahn et al. Involuntary arm
elevation during yawning in a hemiplegic
patient.
-
- -Na-Yeon
Jung, Bo-Young Ahn et al. A case of
parakinesia brachialis oscitans. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 2012;114(2):156-158.
-
- Patel
A, Garg I. Exploring Parakinesia
Brachialis Oscitans: Insights into
Post-Stroke Phenomena. Neurology 2025;104 (7
Supplement 1)
-
- -Salavisa
M, Mohamed B, Allen-Philbey K, Stennett AM,
Campion T, Schmierer K. Parakinesia
Brachialis Oscitans in a Patient With a First
Manifestation of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol
Clin Pract. 2023 Dec;13(6):e200204
-
- -Teive
H, Becker N, Munhoz RP. Parakinesia
Brachialis Oscitants due Brainstem Sroke.
Report of two cases Parkinson Rel Dis
2009;15(Supp 2):S154.
-
- -Thomson
HC Associated movements in hemiplegia :
their origin and physiological significance
Brain 1903;26:515-523.
-
- - Töpper
R, Mull M, Nacimiento W. Involuntary
stretching during yawning in patients with
pyramidal tract lesions: further evidence for
the existence of an independent emotional
motor system. European Journal of Neurology
2003; 10:495-499.
-
- -Tsai
C-C, Lee JD, Chen T. Parakinesia
Brachialis Oscitans and Excessive yawning
From Tumefactive Demyelination. The
Neurohospitalist. 2024;14(1):104-105.
-
- -Walusinski O,
Quoirin E, Neau JP. La parakinésie
brachiale oscitante. Rev Neurol (Paris).
2005;161(2):193-200.
-
- -Walusinski
O, Bogosslavsky J, Neau JP. Hand up !
yawn and raise your arm. The International
Journal of Stroke 2010;5(1):21-27.
-
- -Wu
YT, Chang ST, Chen LC, Li TY. Concurrence
of Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis and
Parakinesia Brachialis Oscitans in a Patient
with Hemorrhagic Stroke. Case Rep Med.
2013;2013:519808.
-
- -Zorzetto
FP, Braatz VL, Walusinski O, Teive HA.
Parakinesia brachialis oscitans during
thrombolytic therapy. BMJ Case Rep.
2013.
-
Parakinésie
brachiale oscitante et syndrome
pseudo-bulbaire
- Robert Thurel (1899-1974), Boudin G.
- Rev Neurol
(Paris)
- 1974;130(11-12):469-70
-
- Chez un de nos malades qui
présente une hémiplégie
gauche totale avec contractures,
syncinésies spasmodiques,
réflexes profonds du cou, se
produisent au niveau des doigts et des
orteils du côté gauche des
mouvements athétosiques dans certaines
circonstances.
-
- C'est ainsi qu'il survienne le matin au
réveil : les doigts s'allongent et
s'écartent ; les orteils,
fléchis en permanence se redressent et
soulèvent les couvertures. Ces
mouvements sont longs et persistent plusieurs
secondes, puis les doigts et les orteils
reprennent leur attitude en flexion. Ils
accompagnent également les
accès de bâillements ; par
compte les efforts volontaires du
côté opposé, où
les actes para volontaires (rires, toux) ne
déclenchent pas ces mouvements mais
des syncinésies globales. Il est
à noter que les conditions
d'apparition de ces mouvements
athétosiques ont quelque analogie :
passage du sommeil à l'état de
veille ou bâillements.
-
- Alajouanine
Th, Thurel R. La diplégie faciale
cérébrale forme corticale de la
paralysie pseudo-bulbaire.
Rev Neurol 1932;38:516-517
-
- Brissaud
E, Marie P. Diplégie faciale
totale avec paralysie
glosso-laryngo-cervicale chez deux
frères. Le Bulletin
Médical 1893;7(96):1081-1084
-
- Les
pseudo-bulbaires
étude clinique et
anatomo-pathologique
- Robert Thurel (1899-1974)
-
 -
|

